What Is Aperture In Camera
The diaphragm is simple. In a nutshell, discontinuity is a device in the lens that measures the amount of calorie-free.
For a better understanding of the performance of such a device, I volition give an case from life. When people expect at the lord's day, they squint their eyes, that is, they reduce the gap through which light passes. If people did not squint, the sun would burn the retina with its strong light. At dark, you need to exercise the opposite - open your optics wider to capture more low-cal, while the pupils also dilate. Optics with large pupils have many animals that demand to see well at night.
Often the diaphragm is also called 'luminous efficiency ' or 'discontinuity' or 'relative hole' or 'number F'. These concepts are strongly related to each other and are synonymous for many photographers. But among them in that location are small-scale differences, described beneath.
Lens aperture Is the ratio of the effective discontinuity of the lens to the focal length of the lens. The reciprocal of the relative discontinuity is called f-number or aperture number.
The relative aperture of the lens is expressed numerically by ratio or fraction. For example, take a lens that has a relative aperture 16 times smaller than its focal length; as a result, the relative aperture can exist numerically written in the following means: 1:xvi or f1 / 16 or f = one: sixteen or F 1:sixteen, etc. d. In that location is no detail divergence in the recording, and every photographer will ever understand what is at stake.
If nosotros take the number opposite to the relative aperture, and so we go the number of aperture. Usually information technology is by this number that photographers directly empathize the general term 'aperture'... If we have the same lens, which has a relative aperture xvi times smaller than its focal length, then its discontinuity number will be equal to 16. And numerically it can be written in the following ways: F16, F / sixteen, 16 (such a 'bare' number aperture is indicated on the lens butt). There is no particular difference in recording.
Some lenses take an aperture ring on their torso. At that place is usually a marker on the ring, consisting solely of aperture numbers (shown in the figure below). Most all mod lenses do not take such a band, and the diaphragm is controlled past the electronics and camera controls.
Usually the concept of 'discontinuity' and 'discontinuity' are synonymous, but in fact there is a sure sacristy betwixt them. And so, the diaphragm is just responsible for geometric aperture (the ratio of linear geometric indicators). And not only the discontinuity is responsible for the overall 'real aperture' of the lens, but also many other factors: the optical design of the lens, the percentage of calorie-free reflection and transmission by the lens, the drop in the aperture number when focusing at dissimilar distances, the percentage of light absorption by the photo filter, etc. More than details almost the difference between the concepts of 'discontinuity' and 'aperture' can be constitute in the section near 'T-anxiety'.
The aperture is sometimes likewise called the 'Lens Aperture' (Latin 'Apertura' - 'Hole'). Therefore, on many cameras, the metering manner exposure с aperture priority called 'A' or 'AV'-'Aperture 5alue '-' Discontinuity Value '. Details almost this style are described in the department 'P, A (AV), Due south (Goggle box), M'.
Please note that the magnitude of the front lens of the lens and, in fact, the magnitude of the front end low-cal filter accept no direct relation to the aperture ratio of the lens. Unlike lenses with the same focal length and the same maximum aperture tin can have completely unlike diameters for their front lenses. For example, take two form l mm F / 1.4 lenses: Nikon AF Nikkor 50mm one: 1.4D и Sigma 50mm 1: 1.4 DG HSM EX... The starting time has a tiny filter diameter - 52 mm, the 2nd has a huge one - 77 mm. But their discontinuity (practically - maximum discontinuity) will exist the same.
What is the diaphragm?
By the mechanical part of the diaphragm device is understood a changing circular hole in the lens. Typically, the hole opens and closes with the petals. In this case, the petals are called diaphragm blades, and the diaphragm itself is 'iris' (from the English 'iris' - 'iris'). The number and roundness of the aperture blades determines how much the hole will be formed round. The stronger the rounding of the diaphragm opening, the better. Professionals often refer to the diaphragm simply as'pigsty'since it is real, a kind of pigsty that changes its size and doses the amount of calorie-free.
What the diaphragm affects:
- The corporeality of light that the lens can allow through over time.
- To command the depth of sharply depicted space (GRIP)
- The effulgence of the image in the optical viewfinder
- On prototype quality, specially on its sharpness, aberration, vignetting, bokeh and various visual effects.
International monetary fund impact
As information technology turned out, the aperture affects not only the amount of low-cal, but too the depth of field. The smaller the number F, the smaller the depth of field. The larger the F number, the greater the depth of field. This is one of the primary techniques in photography to control the point of attention in the photo. Information technology is very important to be able to manage GRIP for portraits where you demand to focus on a person. Macro photographers are well aware what is DOF, they have to shoot on very tightly closed apertures to increase the depth of field. In general, where write most DOFwrite about blurred groundwork. You lot can read the all-time mode to take pictures with a blurry background in my commodity - Taking Pictures with Blurred Background.
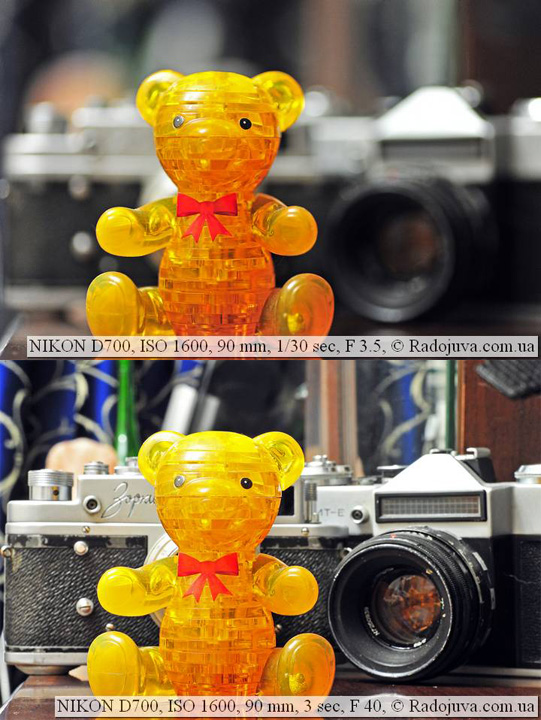

Blurring the background at different apertures
Depth of field preview
Typically, modern cameras have the ability to focus with a fully open aperture. When a moving picture is taken, the camera'due south automation closes the iris to the set value. To encounter how the images volition look when the discontinuity is airtight, you lot can sometimes utilize the aperture repeater. This allows you to look into the viewfinder (optical or electronic) without a film how the picture will look when the camera closes the iris. Y'all can read more about depth of field preview.
Aperture for film enhancement
Discontinuity is understood to mean simply changing the discontinuity value. Using aperture control, y'all tin accomplish a sharper image from the lens. Basically, the sharpest epitome is achieved somewhere at the average aperture of a lens. At their largest aperture, lenses suffer from chromatic aberrations and vignetting. When endmost the diaphragm HA and vignetting practically disappears. At very minor apertures, lenses suffer from diffraction loss of sharpness. Also, when you close (decrease the aperture), not only the sharpness increases, simply besides the contrast of the motion-picture show. A large aperture allows sighting through the optical viewfinder without any bug, since the lens gives a lot of light and the entire frame is clearly visible through the peephole. Yous can but view with an aperture below F5.6 through the optical viewfinder in good lighting conditions. Also, pictures with a larger aperture can appear brighter and more than saturated - this effect is associated with smoother transitions in pictures from nighttime to light areas.
Bokeh and discontinuity continued forever
Aperture greatly affects the bokeh design. Usually the best bokeh for the lens is achieved at the maximum open aperture. In this instance, the concrete hole itself is as round as possible. When closing the diaphragm, the diaphragm petals instead of a circle form different polyhedrons. These polyhedra are clearly visible in the blur zone. Very often such polyhedra are called nuts, washers and circular saws.
Since in cheap lenses there is a small number of discontinuity blades, commonly no more than 5-6, then in the mistiness zone figures appear exactly similar "nuts". Those lenses that on closed apertures requite the correct circular luminous spots in the mistiness zone, for example, can exist attributed to them. Nikon AF DC-Nikkor 105mm 1: 2 D Defocus Image Command or Tair-11A ii,8 / 135. In new lenses, information technology is very rare to find a big number of aperture blades, but now they make more rounded blades, which, fifty-fifty with a pocket-size number of them, give a round hole.
Below are my photographs taken with different cameras and lenses and taken at different values of the number F. Shooting options (EXIF) for each photo are indicated in the bottom line.
Aperture in phone cameras and other modest devices
The diaphragm is a mechanical function of the lens, it cannot be done programmatically. Almost all phones lack a concrete diaphragm device. Many 'soap dishes' besides lack a diaphragm. How to exist? Usually the camera in such devices doses the corporeality of light only shutter speed and a variation of the ISO value, and the aperture value itself is constantly fixed at the maximum value. For case, on my Nokia 7610 it is indicated that F2.8, because the camera e'er shoots at F2.8.
How to adjust the discontinuity in the camera?
In cameras, information technology is responsible for the diaphragm F number (discontinuity number)... It shows how many times the diameter of the relative aperture is less than the focal length of the lens, on the lens it is written equally f1 / 1.iv or f1 / v.6, sometimes you lot can discover the spelling f = 1: 6.3 or 1: 5.half-dozen, or f / sixteen, f / 3.2. Often, lenses or cameras only have one f-number, such every bit' one.4 'or '16.0 .eight.0'. Usually, the aperture number is written with a large letter 'F' without fractions, for example, F 1, and the relative aperture is more frequently written through a small alphabetic character 'f', for example f eleven:XNUMX (at that place tin be any spellings). The easiest way to accommodate the aperture is by putting the camera in aperture priority mode. On the main command wheel of the photographic camera, or in the menu of the camera, this way is indicated past 'A' or 'AV'. To make it piece of cake to remember, you can merely say: Aperture means y'all need to turn on the 'A' manner. Details about the creative discontinuity priority mode are written here.
'Low-cal' and 'dark', 'fast' and 'slow' lenses
The maximum aperture value determines how much the lens can be used in poor lighting weather condition. Lenses with a large aperture are called 'vivid' or 'bright', usually an F value should be below 2.8. That is, lenses with maximum apertures F1.4, F1.viii, F2.0, F2.2, F2.v, F2.eight are chosen fast or just bright. Everything below F1.4 is called super fast. Super fast lenses include Nikon 50mm f / ane.two AI-Southward Nikkor or Catechism Lens FD 55mm f / 1.2 SSC. Lenses that have an aperture value of F / 2.8 to F / 5.6 are chosen ordinary. medium-discontinuity lenses, these lenses can be attributed Nikon 24-85mm f / 2.8-4DAFIF Nikkor or Nikon 300mm f / 4.5 Nikkor-H Nippon Kogaku Japan Auto Non-AI. Lenses with a maximum aperture less than F / 5.half dozen are called low-aperture or 'dark'. These lenses include MS MTO-eleven 1000mm F10.0. Past the manner, information technology is very difficult to make a fast zoom, in more than item here.
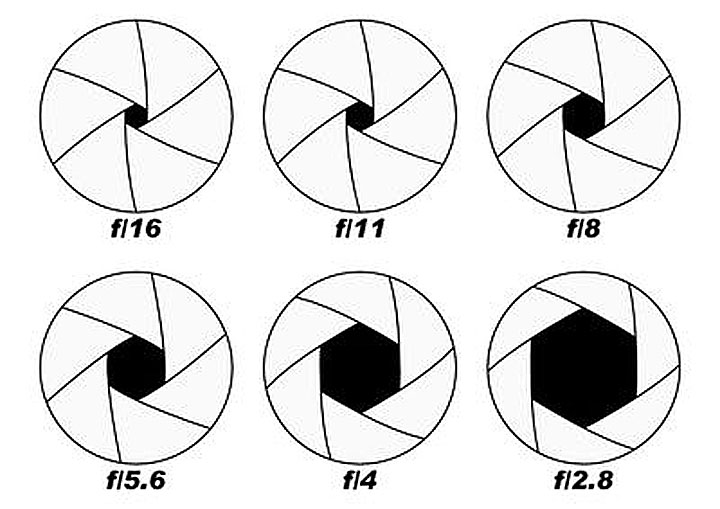
Different holes for different values of the number F
Since aperture affects speed excerpts, and so the lenses are even so divided into fast and slow. A fast lens means that you lot can use information technology to shoot an image with a short shutter speed (with 'fast' shutter speed). And under slow, that it can be used to accept a photo with a long ('slow' shutter speed). If you lot ready the ISO value, it depends on the aperture extract, and the brighter the lens, the faster it is. And the darker the lens, the slower it is.
The difference in aperture ratio
The difference in aperture and other photographic variables is usually measured in feet. When changing the aperture by one finish excerpt will change in twice... Besides, if you change the aperture past 1 stop, you tin can change the ISO past two instead of the shutter speed. Information technology is very important to notation that the departure in aperture values is not linear, simply quadratic. Take two apertures F / 5.6 and F / ii.8, it would seem that the departure in geometric discontinuity is v.half dozen / 2.8 = 2 times, only this is not true. On aperture affects the surface area of the circumvolve formed by the diaphragm, and not its diameter. The number F is associated only with the diameter. To calculate the difference in area you need to take the squares of the diameters. Therefore, it turns out that the departure in discontinuity ratio between F / 5.vi and F / 2.viii is (5,half dozen * 5,6) / (two,8 * ii,eight) = four times. Here is such a play a trick on. How to remember this? There are two ways out, either by dividing the squares of the F numbers, or by first dividing the F numbers and then squaring the result. Why am I bored with calculations - but because often amateur photographers take no idea how many times one lens is 'lighter' or 'darker' than another lens.
Also, experienced photographers know nigh the so-called aperture serial of numbers, in which every two side by side numbers F differ by one stop.
A number of numbers F: i, i.4, 2, 2.8, 4, v.half-dozen, 8, 11, 16, 22, 32, 46, etc.
Gilded Rule:
Aperture and shutter speed are bound by the gilded rule. To keep correct exposure with the same ISO, you must either close the discontinuity and increase the shutter speed, or, conversely, open up the aperture and reduce the shutter speed.
Shut, open, increment decrease - no need to exist confused
Everything is very simple. Closing or decreasing the aperture means increasing the F number. The aperture was F2.8, when it was airtight, information technology became F5.6, it was closed even stronger, it became F16.0, etc. For example, there is the phrase 'covered the hole by ii stops', information technology is deciphered as follows: 'made the number F large and reduced the area of the hole by 4 times'. The chief thing is not to get confused, when the aperture opens, the F number decreases. And when the diaphragm closes, the F-number increases. For case, the aperture was F32.0, when information technology was opened, it became F8.0, when it was opened even stronger, it became F5.half-dozen.
What to do - goose egg is articulate
If you have a DSLR, turn the camera backwards and so that you are looking into the lens, press the shutter button (accept a moving picture) and you will see the hole in the lens shut and open - this is how the aperture works. If yous peered into your lens and did not run into anything, then below is a irksome-motion video, where you can conspicuously see how the aperture works during shooting. In the video, the petals close to F / xvi and form a very 'small hole':
I shoot mainly on the Nikon system, because I accept a couple of interesting manufactures on the site almost the intricacies of the discontinuity on Nikon cameras:
- The method of performance of the device aperture on Nikon digital SLR cameras and its effect on video recording
- Nikon 'E' Lenses with Electromagnetic Iris Control
- An interesting aperture on Nikon digital SLR cameras
- G-blazon and Non-G type lenses (with aperture band and without aperture ring)
- Piece of work with one-time Nikon lenses such as AI, AI-S, Non-AI, PRE-AI, AI-Converted, which transmit or do not transmit aperture value to the camera
In the comments, you can ask a question on the topic and they volition definitely answer you, and y'all tin can as well limited your stance or share your experience. Many little things for a photo tin can be found on AliExpress.
conclusions
Diaphragm Is a luminous flux dispenser that affects exposure, GRIP, brightness of the optical viewfinder and image quality. In general, if y'all don't shoot at different values of the number F, yous don't really know what it is :)
Material prepared Arkady Shapoval... Look for me on Youtube | Facebook | Instagram | Twitter.
Source: https://radojuva.com/en/2012/02/diafragma/
Posted by: markshowere.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Aperture In Camera"
Post a Comment